Feature Store: Trụ cột giải quyết Training–Serving Skew trong MLOps
I. Giới thiệu: Thách thức cốt lõi trong Machine Learning Production
Hành trình từ mô hình thử nghiệm (Experiment) trong Jupyter Notebook đến hệ thống dự đoán thời gian thực (Serving) trong môi trường sản xuất thường gặp phải một "vết nứt" nguy hiểm.
Vấn đề cốt lõi không nằm ở thuật toán, mà là sự thiếu nhất quán của dữ liệu và các đặc trưng (Features).
Vấn đề: Training–Serving Skew
Logic tính toán đặc trưng trong môi trường huấn luyện (Offline) – xử lý theo lô/batch – và môi trường phục vụ (Online) – xử lý thời gian thực với độ trễ thấp – thường là hai hệ thống độc lập, có thể khác biệt về ngôn ngữ hoặc hạ tầng.
Training–Serving Skew là hiện tượng hiệu suất mô hình sụt giảm trên thực tế do sự khác biệt trong logic xử lý đặc trưng giữa hai môi trường này.
Một khác biệt nhỏ trong cách xử lý giá trị null, làm tròn số, hoặc tổng hợp dữ liệu cũng đủ để làm hiệu suất mô hình suy giảm nghiêm trọng.
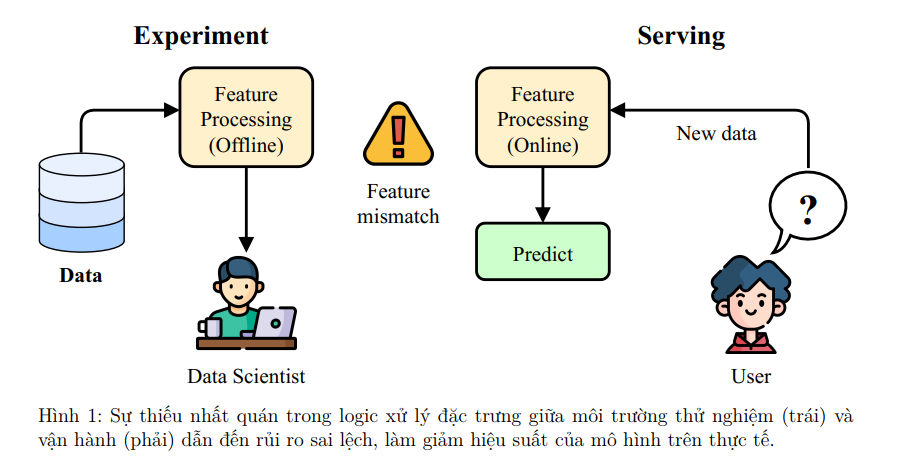
Để giải quyết những thách thức này và kết nối hiệu quả giữa giai đoạn nghiên cứu và giai đoạn vận hành, một thành phần hạ tầng chuyên biệt đã ra đời và trở thành phần cốt lõi trong các hệ thống MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) hiện đại: Feature Store. Bài viết này sẽ giới thiệu về Feature Store, bắt đầu từ vai trò và vị trí của nó trong hệ sinh thái MLOps, trình bày các chức năng chính, và cuối cùng là hướng dẫn thực hành chi tiết với Feast, một trong những Feature Store mã nguồn mở hàng đầu.
Note: Bảng chú thích thuật ngữ cốt lõi
| Thuật ngữ | Giải thích |
|---|---|
| MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) | Bộ quy tắc và công cụ để tự động hóa, chuẩn hóa vòng đời của hệ thống Machine Learning, từ huấn luyện đến triển khai và giám sát. |
| Feature Store | Hệ thống trung tâm để quản lý, lưu trữ, và cung cấp các đặc trưng một cách nhất quán cho cả việc huấn luyện và dự đoán. |
| Feature (Đặc trưng) | Một biến đầu vào có thể đo lường được, dùng làm tín hiệu cho mô hình học và dự đoán (ví dụ: tuổi khách hàng, số tiền giao dịch trung bình trong 1 giờ). |
| Entity | Một đối tượng kinh doanh (ví dụ: một khách hàng, một sản phẩm) mà các đặc trưng mô tả, đóng vai trò là khóa kết nối (join key) để tra cứu đặc trưng. |
| Training-Serving Skew | Hiện tượng hiệu suất mô hình sụt giảm trên thực tế do sự khác biệt trong logic xử lý đặc trưng giữa môi trường huấn luyện và môi trường phục vụ. |
| Offline Store | Kho chứa dữ liệu lịch sử của các đặc trưng, tối ưu cho việc truy vấn các tập dữ liệu lớn nhằm mục đích huấn luyện mô hình. |
| Online Store | Kho chứa chỉ lưu giá trị mới nhất của các đặc trưng, tối ưu cho việc truy vấn với độ trễ cực thấp (low latency) để phục vụ dự đoán thời gian thực. |
| Materialization | Quá trình tính toán và nạp các giá trị đặc trưng từ Offline Store vào Online Store để phục vụ cho việc dự đoán thời gian thực. |
| Point-in-time Correctness | Tính năng đảm bảo khi tạo dữ liệu huấn luyện, giá trị đặc trưng được lấy đúng tại thời điểm trước khi sự kiện xảy ra, tránh rò rỉ dữ liệu từ tương lai. |
II. Giải pháp: Feature Store
Feature Store là một hệ thống trung tâm được thiết kế để quản lý, lưu trữ, và cung cấp các đặc trưng một cách nhất quán cho cả việc huấn luyện mô hình và dự đoán thời gian thực.
Nó đóng vai trò là cầu nối trung tâm giữa dữ liệu và mô hình trong kiến trúc MLOps hiện đại.
Feature Store = Database dành riêng cho Feature ML, nhưng được thiết kế đặc biệt để:
- Giữ tính nhất quán (Consistency) giữa dữ liệu dùng trong huấn luyện (training) và dự đoán (serving).
- Tự động hóa (Automation) quy trình trích xuất và tái sử dụng đặc trưng.
- Chia sẻ và cộng tác (Collaboration) giữa các nhóm Data Scientist, Data Engineer, và MLOps.
- Giám sát (Monitoring) để phát hiện drift và đảm bảo chất lượng dữ liệu đầu vào mô hình.
Ví dụ trực quan Giả sử bạn muốn dự đoán khách hàng có rời mạng (churn) hay không.
Một số đặc trưng bạn cần là:
| Feature Name | Description | Nguồn dữ liệu |
|---|---|---|
| tenure_months | Số tháng khách hàng đã sử dụng dịch vụ | Database CRM |
| monthly_charge_avg | Trung bình hóa đơn 3 tháng gần nhất | Data Warehouse |
| num_support_calls | Số lần khách hàng gọi tổng đài | API Logs |
| is_premium_user | Khách hàng có gói cước cao cấp không | Subscription DB |
Trong môi trường huấn luyện, bạn cần các đặc trưng này theo thời gian (lịch sử). Trong môi trường triển khai (real-time), bạn cần phiên bản mới nhất của các đặc trưng đó cho khách hàng vừa truy cập.
Nếu hai nơi tính toán khác nhau (ví dụ làm tròn, fill NA khác nhau), mô hình sẽ bị Training–Serving Skew.
Code mô phỏng quy trình xây dựng Feature Store bằng Feast cho bài toán Churn Prediction:
1️ Import Feast components
from feast import FeatureStore, Entity, Field, FeatureView, FileSource
from feast.types import Float32, Int64
2️. Định nghĩa Entity (đối tượng chính)
python
Copy code
customer = Entity(name="customer_id", join_keys=["customer_id"])
3️. Định nghĩa nguồn dữ liệu
python
Copy code
churn_source = FileSource(
path="data/telco_features.parquet",
timestamp_field="event_timestamp"
)
4️. Định nghĩa FeatureView (nhóm đặc trưng)
python
Copy code
churn_fv = FeatureView(
name="customer_churn_features",
entities=[customer],
ttl=None, # Time-to-live
schema=[
Field(name="tenure_months", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="monthly_charge_avg", dtype=Float32),
Field(name="num_support_calls", dtype=Int64),
],
source=churn_source,
)
5️. Tạo Feature Store instance
python
Copy code
store = FeatureStore(repo_path=".")
6️. Lấy dữ liệu huấn luyện
python
Copy code
training_df = store.get_historical_features(
entity_df="data/entity_df.parquet",
features=[
"customer_churn_features:tenure_months",
"customer_churn_features:monthly_charge_avg",
"customer_churn_features:num_support_calls",
],
).to_df()
7️. Truy xuất đặc trưng thời gian thực (serving)
python
Copy code
online_features = store.get_online_features(
features=[
"customer_churn_features:tenure_months",
"customer_churn_features:monthly_charge_avg",
"customer_churn_features:num_support_calls",
],
entity_rows=[{"customer_id": "12345"}],
).to_dict()
print("Online feature vector:", online_features)
---
Kết quả là một Feature Vector đồng nhất giữa training và serving:
{
"tenure_months": [12],
"monthly_charge_avg": [35.2],
"num_support_calls": [4]
}
III. Kiến trúc và Các thành phần cốt lõi của Feature Store
Feature Store được tích hợp vào vòng đời MLOps để đảm bảo tính nhất quán và khả năng tái sử dụng đặc trưng.
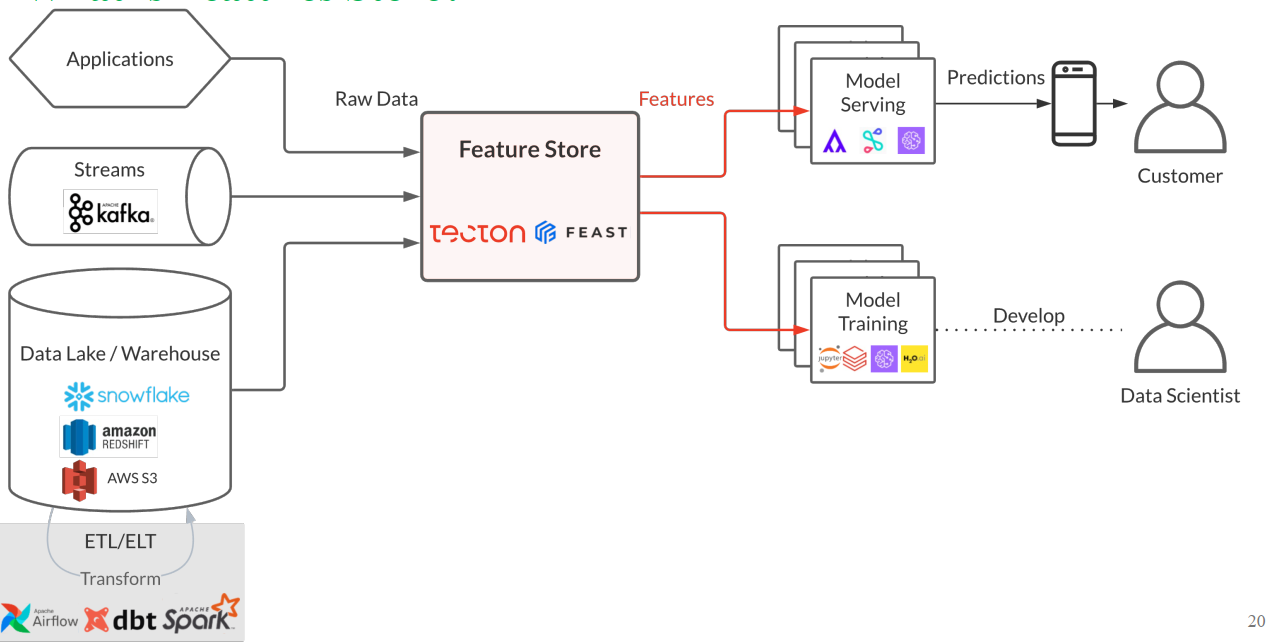
Hình 2: Feature Store đóng vai trò trung tâm, kết nối các nguồn dữ liệu thô (Applications, Streams, Data Lake/Warehouse) với các quy trình Model Serving và Model Training [1].
1. Storage (Lớp Lưu trữ)
Trừu tượng hóa hạ tầng dữ liệu, gồm hai kho chính:
Offline Store:
- Lưu trữ dữ liệu lịch sử của đặc trưng (nhiều tháng/năm).
- Tối ưu cho truy vấn dữ liệu lớn phục vụ huấn luyện, backfilling, validation.
- Thường sử dụng BigQuery, Snowflake, S3.
Online Store:
- Lưu trữ giá trị mới nhất của các đặc trưng.
- Tối ưu cho truy vấn độ trễ thấp (low-latency) phục vụ dự đoán thời gian thực.
- Triển khai bằng Redis, DynamoDB.
2. Serving (Lớp Phục vụ)
Cung cấp dữ liệu đặc trưng cho mô hình:
Offline Serving:
- Cung cấp SDK lấy dữ liệu lịch sử lớn.
- Đảm bảo Point-in-time Correctness – giá trị đặc trưng được lấy đúng tại thời điểm trước khi sự kiện xảy ra.
Online Serving:
- Cung cấp API hiệu năng cao để lấy Feature Vector trong thời gian thực.
3. Transformation (Lớp Biến đổi)
Quản lý logic biến đổi dữ liệu thành đặc trưng, giúp tái sử dụng mã nguồn giữa training và serving.
- Batch Transformations: Áp dụng trên dữ liệu tĩnh (lịch sử).
- Streaming Transformations: Áp dụng trên dữ liệu dòng (Kafka) để tính đặc trưng gần thời gian thực.
- On-demand Transformations: Tính đặc trưng “theo yêu cầu” tại thời điểm dự đoán.
4. Registry (Lớp Đăng ký)
Trung tâm metadata – nguồn duy nhất cho thông tin đặc trưng.
- Vai trò: Catalog để nhóm cộng tác, tái sử dụng định nghĩa đặc trưng.
- Nội dung: Lưu metadata về feature definitions, entities, data sources, transformation logic.
5. Monitoring (Lớp Giám sát)
Theo dõi sức khỏe và chất lượng dữ liệu:
- Feature Drift Monitoring: Phát hiện sự thay đổi phân phối đặc trưng giữa Offline và Online Store.
- Operational Monitoring: Theo dõi latency, throughput, lỗi hệ thống.
IV. Feast: Giải pháp Feature Store mã nguồn mở hàng đầu
Feast (Feature Store for Machine Learning) là giải pháp mã nguồn mở hàng đầu, nổi bật với triết lý thiết kế linh hoạt.
1. Triết lý cốt lõi
Feast không phải là nền tảng "tất cả trong một", mà là một lớp điều phối mỏng, kết nối và tái sử dụng hạ tầng dữ liệu sẵn có.
- Offline Store: BigQuery, Snowflake, Data Lake
- Online Store: Redis, DynamoDB
2. Các đối tượng định nghĩa chính (Feast Objects)
- Entity: Đại diện cho đối tượng kinh doanh (customer_id, transaction_id).
- DataSource: Nguồn dữ liệu vật lý (Parquet, BigQuery).
- Feature: Thuộc tính của Entity, dùng làm đầu vào mô hình.
- FeatureView: Nhóm Entity, DataSource, Features thành đơn vị logic.
- FeatureService: Gộp các FeatureViews phục vụ mô hình cụ thể.
3. Các lệnh CLI và Hàm SDK cốt lõi
| Lệnh/Hàm | Chức năng | Mục đích |
|---|---|---|
feast init <tên_project> |
Khởi tạo project Feast mẫu | Thiết lập ban đầu |
feast apply |
Đăng ký định nghĩa vào Registry, cập nhật hạ tầng | Quản lý vòng đời |
feast materialize <start> <end> |
Nạp dữ liệu từ Offline sang Online Store | Cập nhật dữ liệu |
store.get_historical_features() |
Lấy dữ liệu huấn luyện (Point-in-time Correctness) | Training |
store.get_online_features() |
Lấy vector đặc trưng mới nhất | Serving thời gian thực |
V. Thực hành: Xây dựng Pipeline Churn Prediction với Feast (FeastFlow)
Mô phỏng pipeline dự đoán hành vi rời mạng (Telco Churn) bằng Feast.
1. Chuẩn bị Dữ liệu (Extract & Transform)
- Extract: Tải dữ liệu Telco Customer Churn từ Kaggle.
- Transform:
- Xử lý Missing Value (ví dụ:
TotalCharges→ dạng số, điền 0). - Mã hóa (Binary, One-hot Encoding).
- Tạo đặc trưng phái sinh (Derived Features):
customer_tenure_ratio,monthly_charge_avg, ... - Lưu dưới định dạng Parquet.
Code:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import os
import shutil
# --- Cấu hình và Tải Dữ liệu ---
DATA_DIR = "data"
PROCESSED_DATA_FILE = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, "telco_churn_processed.parquet")
RAW_DATA_FILE = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, "WA_Fn-UseC_-Telco-Customer-Churn.csv")
def download_data():
"""Giả lập việc tải dữ liệu từ Kaggle."""
# Trong môi trường thực tế, bạn sẽ dùng thư viện như `kagglehub` hoặc `opendatasets`
# để tải file CSV. Ở đây, ta giả định file đã được đặt trong thư mục data/
if not os.path.exists(DATA_DIR):
os.makedirs(DATA_DIR)
print(f"Thư mục '{DATA_DIR}' đã được tạo.")
# Giả lập: Nếu file CSV không tồn tại, tạo một file trống để tránh lỗi.
if not os.path.exists(RAW_DATA_FILE):
print("Tạo file CSV giả lập. Vui lòng thay thế bằng dữ liệu Telco Churn thực tế.")
# Tạo DataFrame mẫu để mô phỏng cấu trúc cần thiết
data = {
'customerID': [f'C{i:05d}' for i in range(100)],
'gender': np.random.choice(['Male', 'Female'], 100),
'SeniorCitizen': np.random.randint(0, 2, 100),
'Partner': np.random.choice(['Yes', 'No'], 100),
'Dependents': np.random.choice(['Yes', 'No'], 100),
'tenure': np.random.randint(1, 73, 100),
'PhoneService': np.random.choice(['Yes', 'No'], 100),
'MonthlyCharges': np.random.rand(100) * 100,
'TotalCharges': (np.random.rand(100) * 5000).astype(str),
'InternetService': np.random.choice(['DSL', 'Fiber optic', 'No'], 100),
'Contract': np.random.choice(['Month-to-month', 'One year', 'Two year'], 100),
'Churn': np.random.choice(['Yes', 'No'], 100)
}
df_raw = pd.DataFrame(data)
df_raw.to_csv(RAW_DATA_FILE, index=False)
print("Tải dữ liệu hoàn tất.")
def transform_data(df):
"""Xử lý dữ liệu thô và tạo đặc trưng."""
# 1. Tạo Metadata bắt buộc: customerID và event_timestamp
print("-> Xử lý Metadata: event_timestamp và customerID...")
# 'customerID' đã có trong dữ liệu Telco Churn và sẽ là Entity.
df.dropna(subset=['customerID'], inplace=True)
# Tạo event_timestamp giả lập: Dùng thời gian hiện tại và trừ đi số tháng tenure
now = datetime.now()
df['event_timestamp'] = df['tenure'].apply(lambda x: now - timedelta(days=x * 30))
df['created_timestamp'] = now
# 2. Xử lý thiếu và Chuyển đổi kiểu dữ liệu
print("-> Xử lý thiếu và chuyển đổi kiểu dữ liệu...")
df['TotalCharges'] = pd.to_numeric(df['TotalCharges'], errors='coerce')
df['TotalCharges'].fillna(0, inplace=True)
# 3. Mã hóa (Encoding)
print("-> Mã hóa các cột phân loại...")
# Binary encoding
binary_mapping = {'Yes': 1, 'No': 0, 'Female': 1, 'Male': 0}
binary_columns = ['gender', 'Partner', 'Dependents', 'PhoneService', 'PaperlessBilling', 'Churn']
for col in binary_columns:
if col in df.columns:
df[col] = df[col].map(binary_mapping).fillna(df[col])
# One-hot encoding cho các cột đa giá trị
categorical_columns = ['InternetService', 'Contract', 'PaymentMethod']
df = pd.get_dummies(df, columns=categorical_columns, prefix=categorical_columns)
# 4. Tạo Đặc trưng phái sinh (Derived Features)
print("-> Tạo đặc trưng phái sinh...")
max_tenure = df['tenure'].max()
df['customer_tenure_ratio'] = df['tenure'] / max_tenure
df['monthly_charge_avg'] = np.where(
df['tenure'] > 0,
df['TotalCharges'] / df['tenure'],
df['MonthlyCharges']
)
service_cols = [col for col in df.columns if any(s in col for s in ['PhoneService', 'InternetService', 'OnlineSecurity'])]
df['total_services'] = df[service_cols].apply(lambda x: (x == 1).sum(), axis=1)
# 5. Lựa chọn và Đổi tên cột
final_cols = [
'customerID', 'event_timestamp', 'created_timestamp', 'Churn',
'tenure', 'MonthlyCharges', 'TotalCharges', 'SeniorCitizen',
'gender', 'Partner', 'Dependents',
'customer_tenure_ratio', 'monthly_charge_avg', 'total_services'
]
final_cols.extend([col for col in df.columns if col not in final_cols and any(c in col for c in categorical_columns)])
final_cols = list(set(final_cols).intersection(df.columns))
df = df[final_cols].copy()
return df
def run_prepare_data():
"""Thực thi toàn bộ quy trình chuẩn bị dữ liệu."""
download_data()
df_raw = pd.read_csv(RAW_DATA_FILE)
df_processed = transform_data(df_raw)
print(f"\n-> Lưu trữ dữ liệu đã xử lý vào '{PROCESSED_DATA_FILE}' ({len(df_processed)} hàng)...")
df_processed.to_parquet(PROCESSED_DATA_FILE, index=False)
print("Chuẩn bị dữ liệu hoàn tất.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_prepare_data()
2. Định nghĩa Feature Repository
- Sử dụng
feast initđể tạo project.
# 1. Khởi tạo Feature Repository
# (Lệnh này sẽ tạo thư mục 'feature_repo')
feast init feature_repo
# 2. Di chuyển file dữ liệu đã xử lý vào thư mục feature_repo
# (Giả định 'prepare_data.py' đã chạy và tạo file trong thư mục 'data/')
mv data/telco_churn_processed.parquet feature_repo/data/
# 3. Di chuyển vào thư mục feature repo
cd feature_repo
- Cấu hình:
feature_store.yaml: Online = Redis, Offline = File (Parquet).features.py: Định nghĩaEntity,FileSource,FeatureView.
# feature_repo/feature_store.yaml
project: telco_churn_demo
registry: data/registry.db
provider: local # Dùng 'local' để chạy trên máy tính cá nhân
online_store:
type: sqlite # Dùng SQLite thay vì Redis nếu không cài đặt Docker/Redis.
path: data/online_store.db
# Nếu dùng Redis, thay thế bằng:
# online_store:
# type: redis
# connection_string: localhost:6379
offline_store:
type: file
3. Triển khai Feature Store
- Đăng ký định nghĩa:
feast apply - Nạp dữ liệu Online:
feast materializetừ Parquet → Redis
# feature_repo/features.py
from datetime import timedelta
from feast import Entity, FeatureView, Field, FileSource, ValueType
from feast.types import Int64, Float32, String
# 1. Định nghĩa Entity: customerID
customer = Entity(
name="customerID",
value_type=ValueType.STRING,
description="Unique identifier for a Telco customer",
# Sử dụng join_keys nếu tên cột trong Entity khác tên Entity
join_keys=["customerID"]
)
# 2. Định nghĩa Data Source: Trỏ đến file Parquet
customer_data_source = FileSource(
path="data/telco_churn_processed.parquet", # Path tương đối từ feature_repo
timestamp_field="event_timestamp",
created_timestamp_column="created_timestamp"
)
# 3. Định nghĩa Feature Views
# 3a. Customer Demographics & Base Info
customer_demographics_fv = FeatureView(
name="customer_demographics",
entities=[customer],
ttl=timedelta(days=365*5),
schema=[
Field(name="gender", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="SeniorCitizen", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="Partner", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="Dependents", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="total_services", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="Churn", dtype=Int64), # Target variable
],
source=customer_data_source,
online=True,
)
# 3b. Customer Financials & Tenure
customer_financials_fv = FeatureView(
name="customer_financials",
entities=[customer],
ttl=timedelta(days=365*5),
schema=[
Field(name="tenure", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="MonthlyCharges", dtype=Float32),
Field(name="TotalCharges", dtype=Float32),
Field(name="customer_tenure_ratio", dtype=Float32),
Field(name="monthly_charge_avg", dtype=Float32),
],
source=customer_data_source,
online=True,
)
# 3c. Contract and Service Features (One-Hot Encoded)
# Lưu ý: Lấy các cột one-hot encoding từ file Parquet.
contract_service_fv = FeatureView(
name="contract_service",
entities=[customer],
ttl=timedelta(days=365*5),
schema=[
Field(name="InternetService_DSL", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="InternetService_Fiber_optic", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="InternetService_No", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="Contract_Month_to_month", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="Contract_One_year", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="Contract_Two_year", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="PaymentMethod_Bank_transfer_automatic", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="PaymentMethod_Credit_card_automatic", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="PaymentMethod_Electronic_check", dtype=Int64),
Field(name="PaymentMethod_Mailed_check", dtype=Int64),
],
source=customer_data_source,
online=True,
)
4. Huấn luyện Mô hình
- Dùng
store.get_historical_features()với Entity DataFrame chứaentity_keyvàevent_timestamp. - Feast đảm bảo Point-in-time Join tránh rò rỉ dữ liệu.
- Huấn luyện mô hình (Logistic Regression, Ensemble, ...).
import pandas as pd
from feast import FeatureStore
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
import joblib
import os
# --- Cấu hình ---
FEATURE_REPO_PATH = "feature_repo"
MODEL_FILE = "churn_model.pkl"
PROCESSED_DATA_FILE = os.path.join("data", "telco_churn_processed.parquet")
# Định nghĩa tất cả các features cần dùng
FEATURE_NAMES = [
"customer_demographics:gender",
"customer_demographics:SeniorCitizen",
"customer_demographics:Partner",
"customer_demographics:Dependents",
"customer_demographics:total_services",
"customer_demographics:Churn", # Target variable
"customer_financials:tenure",
"customer_financials:MonthlyCharges",
"customer_financials:TotalCharges",
"customer_financials:customer_tenure_ratio",
"customer_financials:monthly_charge_avg",
"contract_service:InternetService_DSL",
"contract_service:InternetService_Fiber_optic",
"contract_service:InternetService_No",
"contract_service:Contract_Month_to_month",
"contract_service:Contract_One_year",
"contract_service:Contract_Two_year",
"contract_service:PaymentMethod_Electronic_check",
"contract_service:PaymentMethod_Mailed_check",
"contract_service:PaymentMethod_Bank_transfer_automatic",
"contract_service:PaymentMethod_Credit_card_automatic",
]
def train_model():
# 1. Khởi tạo Feature Store và Entity DataFrame
store = FeatureStore(repo_path=FEATURE_REPO_PATH)
# Đọc Entity DF nguồn để lấy customerID, event_timestamp và target variable
entity_df_source = pd.read_parquet(PROCESSED_DATA_FILE)
# Chuẩn bị Entity DataFrame cho Feast (chỉ cần Entity ID và Event Timestamp)
# Lấy thêm cột 'Churn' để làm nhãn (target) sau khi lấy features
entity_df = entity_df_source[['event_timestamp', 'customerID', 'Churn']].rename(
columns={'customerID': 'customerID'}
)
print("Lấy dữ liệu training từ Offline Store (Point-in-time Join)...")
# 2. LẤY DỮ LIỆU TRAINING TỪ OFFLINE STORE CỦA FEAST
# Feast sẽ thực hiện Point-in-time Join
training_data = store.get_historical_features(
entity_df=entity_df.drop(columns=['Churn']), # Chỉ truyền Entity ID và Timestamp
features=[f for f in FEATURE_NAMES if not f.endswith("Churn")] # Loại bỏ target
).to_df()
# Thêm cột Churn (target variable) vào training_data
training_data = pd.merge(
training_data,
entity_df[['customerID', 'event_timestamp', 'Churn']],
on=['customerID', 'event_timestamp'],
how='left'
)
print(f"Kích thước tập dữ liệu huấn luyện: {training_data.shape}")
# 3. HUẤN LUYỆN MÔ HÌNH
print("\nBắt đầu huấn luyện mô hình...")
# Loại bỏ các cột metadata
X = training_data.drop(columns=['event_timestamp', 'customerID', 'Churn'], axis=1)
y = training_data['Churn']
# Chia tập Training/Test
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42, stratify=y
)
# Huấn luyện mô hình
model = LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000).fit(X_train, y_train)
# Đánh giá
print("\n--- Kết quả đánh giá mô hình ---")
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred, target_names=['Stay', 'Churn']))
# 4. LƯU MODEL
print(f"\nLưu model vào file '{MODEL_FILE}'...")
joblib.dump(model, MODEL_FILE)
print("Huấn luyện mô hình hoàn tất.")
# Lưu thứ tự features để đảm bảo Serving nhất quán
feature_order = X.columns.tolist()
with open("feature_order.txt", "w") as f:
f.write("\n".join(feature_order))
print("Lưu Feature Order hoàn tất.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Đảm bảo prepare_data.py đã chạy trước đó
# run_prepare_data() # Gọi nếu cần chuẩn bị lại data
train_model()
5. Dự đoán thời gian thực
- Dịch vụ API (FastAPI, Flask, v.v.) nhận ID thực thể.
- Gọi
store.get_online_features()để lấy Feature Vector mới nhất từ Redis. - Trả kết quả dự đoán Yes/No + Probability.
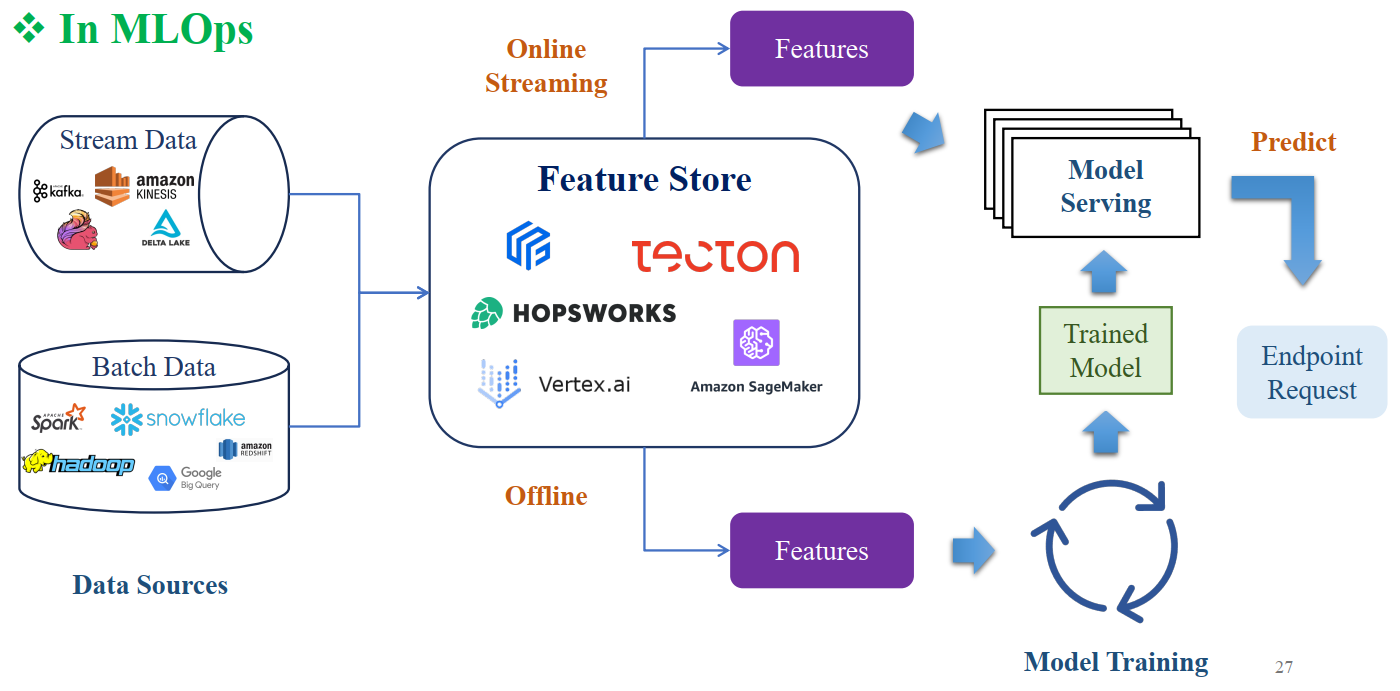
Hình 3: Quy trình Real-time Feature Lookup trong Serving Model, sử dụng Feast và Redis [1].
TÓM TẮT
Kiến trúc và Chức năng Cốt lõi
- Offline Store: Lưu trữ dữ liệu lịch sử cho huấn luyện (Parquet, BigQuery).
- Online Store: Lưu trữ dữ liệu mới nhất cho Serving real-time (Redis).
- Point-in-time Correctness: Đảm bảo dữ liệu huấn luyện đúng thời điểm, tránh rò rỉ dữ liệu.
Feast: Triết lý và Thao tác
- Feast: Lớp điều phối mỏng, tích hợp với hạ tầng dữ liệu có sẵn.
-
Entity: Khóa kết nối (join key) đại diện đối tượng (ví dụ: customer_id).
-
feast apply: Đăng ký Entity/FeatureView vào Registry.
-
store.get_historical_features(): Lấy dữ liệu an toàn cho Training.
-
store.get_online_features(): Lấy Feature Vector mới nhất cho Serving real-time.
Reference
[1] Ảnh được lấy từ tài liệu khóa học AIO Module 05 Tuần 01 và 02.
Chưa có bình luận nào. Hãy là người đầu tiên!